Liechtenstein at a Glance
Facts and Figures
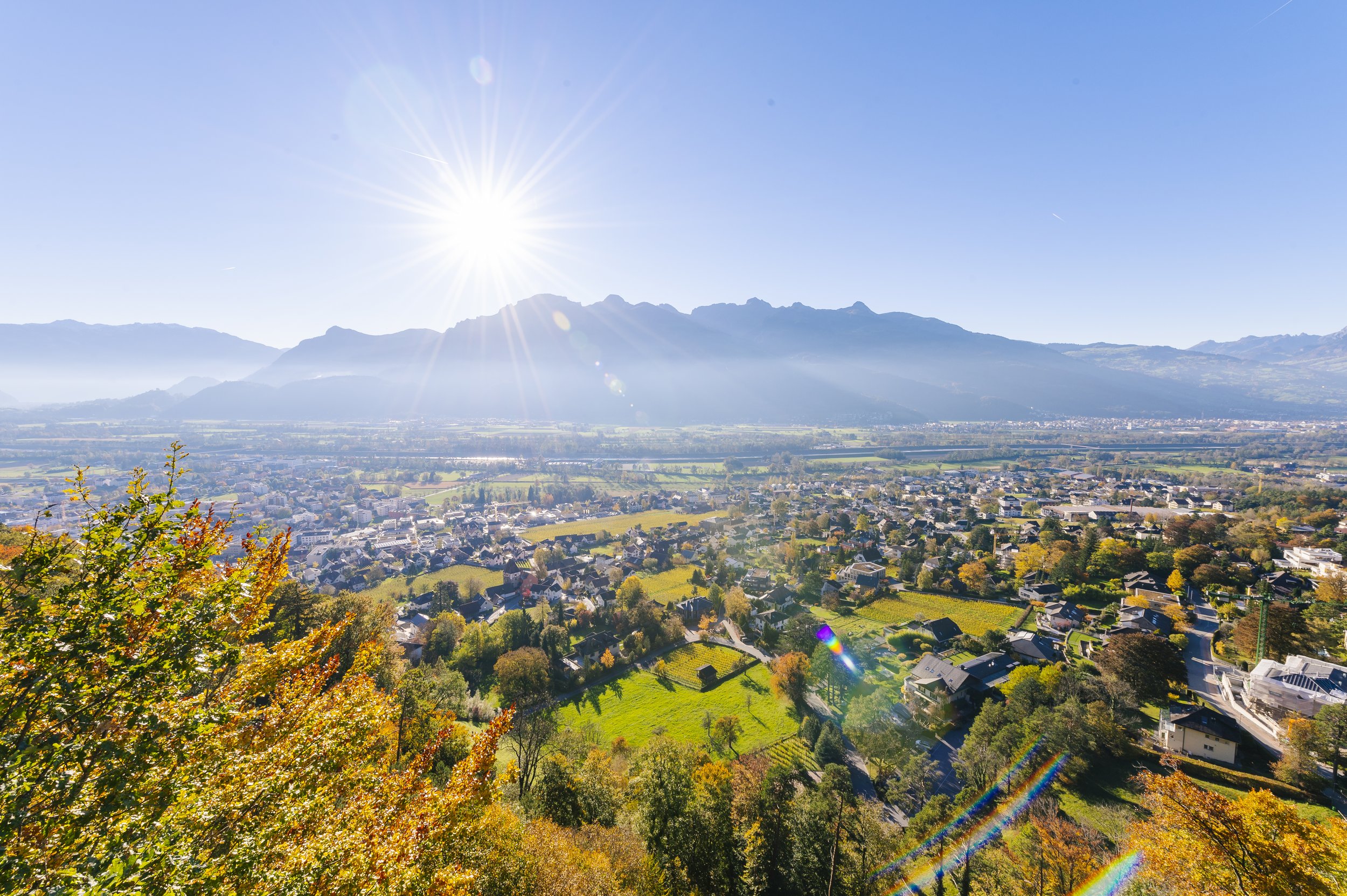
The Principality of Liechtenstein is located in Western Europe between Switzerland and Austria, making Liechtenstein one of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world.
With a total area of 62 square miles, Liechtenstein is roughly the geographic size of Washington, DC.
Liechtenstein has a resident population of roughly 40,000.
The capital of Liechtenstein is Vaduz.
German is the official language, although an Alemannic dialect is the colloquial language.
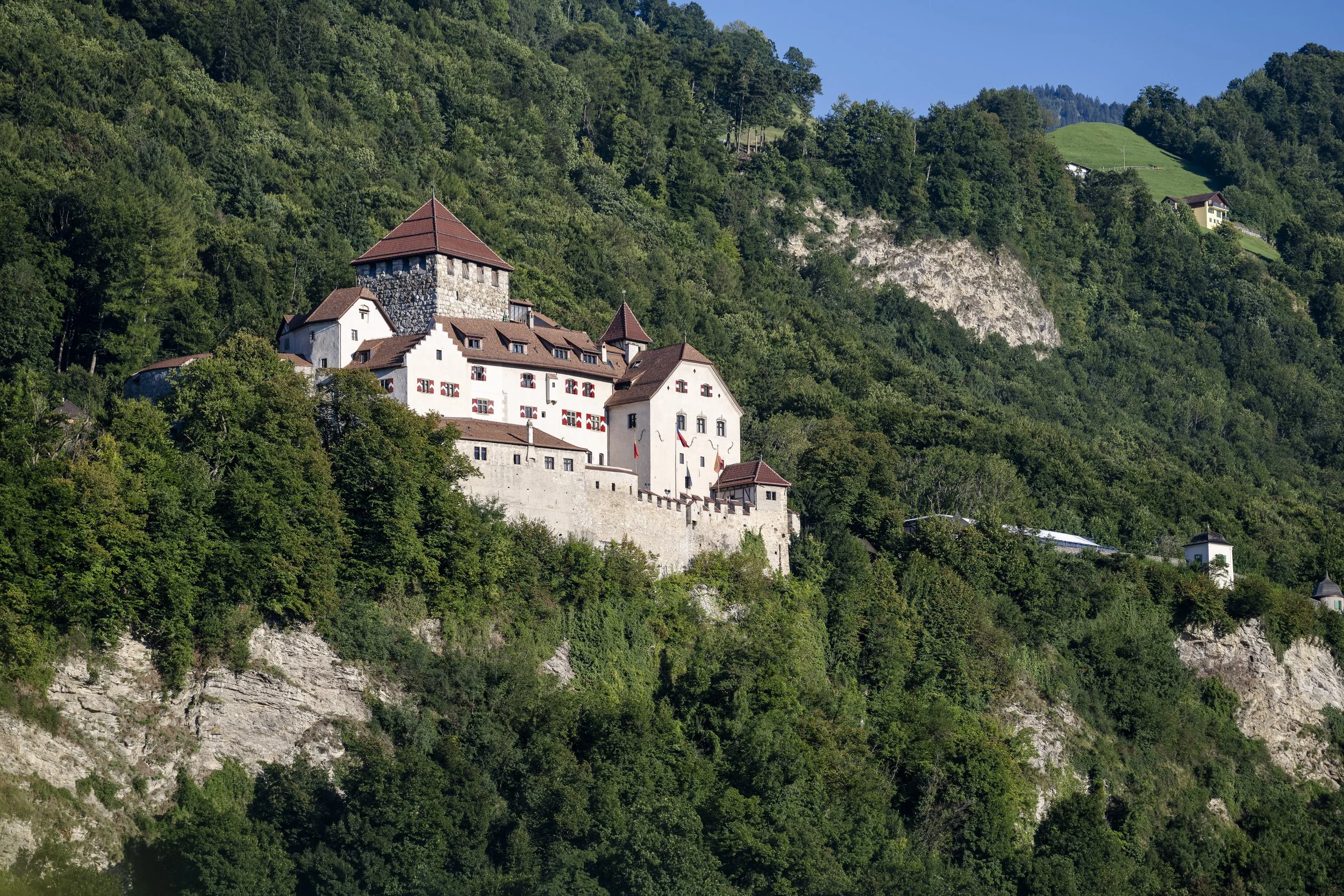
Vaduz Castle - residence of the Princely Family
Government
Liechtenstein is a constitutional hereditary monarchy on a democratic and parliamentary basis, meaning the Reigning Prince and the democratically elected Parliament share power based on a system of checks and balances.
The Head of State is Prince Hans-Adam II. His son, Hereditary Prince Alois, was entrusted as his representative with the exercise of the princely rights appertaining to him in 2004 and has been performing both nationally and internationally the duties of Head of State of the Principality of Liechtenstein.
The Government consists of a five–person cabinet of ministers appointed by the Reigning Prince upon recommendation of the Parliament for four years.
The Government Building in Vaduz
Economy
Although Liechtenstein is a small country, it offers a very favorable economic environment. Unemployment rates are very low.
For a population of about 40,000, there are over 41,352 people employed in Liechtenstein. 23,249 of those employees are foreigners, most of whom commute daily to Liechtenstein from Austria, Switzerland or nearby Germany.
The largest contributor to Liechtenstein’s economy is its manufacturing sector. Along with construction it makes up at 41.6% of the GDP. Second, at 37.3%, is general services (such as consulting, marketing, architecture) and third is its financial services sector at 21.1%.
Liechtenstein’s companies manufacture a variety of products, such as power tools, automotive steering systems, data storage solutions, audio-visual equipment, convenience foods, and dental products.
Economic Structure, 2022
Sector 1 Agriculture 0.2%
Sector 2 Goods 42.2%
Sector 3 Services 57.7%
Culture
In addition to a vibrant economy, Liechtenstein also offers a broad cultural spectrum.
There are museums that exhibit selections from the Princely Family’s extensive art collection, both at the Kunstmuseum in Vaduz and at the Liechtenstein Museum in Vienna. There is a National Museum, as well as museums that focus on the history of skiing and Liechtenstein’s production of artful stamps.
Liechtenstein has a number of theater, film, and music festivals that showcase a variety of local and international talents. Liechtenstein’s alpine backyard also offers a number of outdoor activities ranging from downhill and cross-country skiing to hiking and mountain biking.
For more information and statistical data about Liechtenstein visit "Liechtenstein in Figures" and Economic and Financial Data on Liechtenstein (June 2025).
Inside the Kunstmusuem Liechtenstein (Musuem of Contemporary Art)
Geography
Liechtenstein has an area of 62 square miles (about the same geographic size as Washington, DC), inhabited by roughly 40,000 people. It borders Switzerland in the south and west and Austria in the east and north. The total length of its borders is 47 miles. The country lies at an elevation of 1,486 feet above sea level. The highest mountain in the country is the Grauspitz at 8,527 feet.
The floor of the Rhine Valley covers half of the country. It is the most populous and arable area of Liechtenstein, since the rest of the country consists of rougher alpine terrain. In the Rhine Valley floor, a wide range of transitions between sand, peat, sandy clay, and clay soil can be found. The soils of the Rhine Valley slope consist of detritus, moraine deposits, and some loess. Mountain ranges crossing the country from south to north are foothills of the Rätikon. The Eschnerberg at 2,395 feet stands in the valley, while the mountainous part in the east of the country is formed out of three high-lying valleys.
From a geological standpoint of view the Liechtenstein region is very diverse: The Western and Eastern Alps collide in the middle of Liechtenstein. The boundary runs northeast, from Luziensteig through Vaduz. The largest part of the Alpine area belongs to the East Alpine facies, while the Fläscherberg and Schellenberg jut out of the Rhine Valley as foothills of the Helvetic zone.
Climate
Annual precipitation measures between around 35 and 47 inches. In the mountainous area, precipitation can reach 75 inches. In the winter, temperatures seldom drop below 15 degrees Fahrenheit, while the average temperatures in the summer oscillate between 68 and 82 degrees.
Despite the mountainous location of the country, the climate can therefore be described as mild. It is heavily influenced by the south wind (Föhn). Wine and corn thrive primarily because of the moderating influence of this warm south wind. It lengthens the vegetation period in the spring and the fall. However, it sometimes also has the negative effect of drying out the soil and damaging the cultivation of fruit.
The Princerly House’s Vineyard